一 内容梗概:
这个项目一共有两个需要完成的代码文件,一个是gen_printed_char,另一个是Chinese_OCR。
首先gen__printed_char中的代码的核心就是在网上收集字体文件,即存在Chinese_fonts中的内容。进行泛化(泛化应该是将每个字经过旋转偏移形成各种各样的汉字图像)。下图是一个汉字经过泛化后得到的内容。这时候得到了3755个汉字所对应的泛化图像,第一步完成。
Chinese_ocr是将第一步中得到的3755个汉字所对应的图像进行训练,最后得到一个分类器,随后将待识别的文字图片扔进tmp文件
二 内容细节:
此部分从 gen_printed_char 的init_main部分说起,类似于c语言中的main函数。
首先将这个文件的调用需要一些参数—即相关最终图像所放置的文件,图像旋转的角度等等,作者用了一个args_parse的包。这个包适合处理要输入大量的参数。此部分相关详细内容我放在了这里
1 | if __name__ == "__main__": |
作者定义的类:
1 | def args_parse(): |

1 | # 注意,chinese_labels里面的映射关系是:(ID:汉字) |
Chinese_labels文件是作者按照字典即哈希表样式 每个字对应一个数字 例如 “0 对应着 一,1对应着 丁”,
然后为了便于存储 用pickel模块进行封存,直接打开是乱码,但经过pickel导入就显示内容。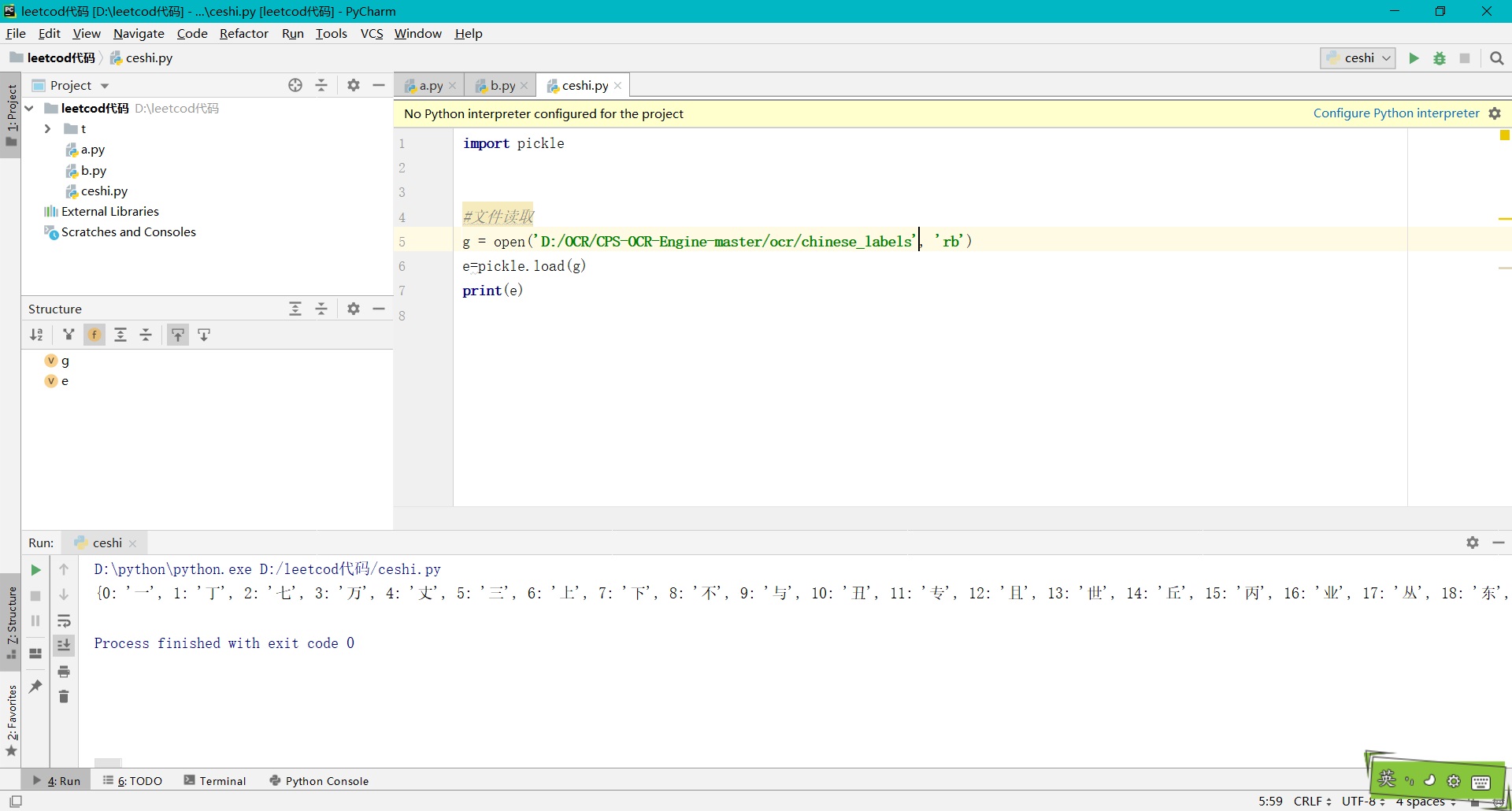
但作者在后面会进行翻转,即汉字对应着·某个数字
1 | label_dict = get_label_dict() |
对于输入的角度不是45吗,然后作者从-45~+45这些角度都进行了添加,即正方向反方向各歪了45
1 | if rotate < 0: |
对于每个字体文件进行看是否能用
1 | # 对于每类字体进行小批量测试 |
1 | 检查字体文件是否可用 |
关于pillow模块的使用可以参照另一篇文档
在上面检测完每种字体文件都可以用之后,下面是生成字体图像的函数,首先与检测文件一样,用pillow生成单独的字与黑色背景,然后组合起来,再然后检测这张图片中这个汉字的最小矩形。
1 | # 生成字体图像 |
中间需要查询的资料:
1 | # 查找字体的最小包含矩形 |
对于每个字的每种字体都先生成一副正常30x30的图像,如果开始是输入的倾斜角度部位0就加大力度生成每个字每种字体每个角度都有一副图像,这个的量就是3755x13x90个图片,然后按照训练比例,我输入的是0.2,就是图片总量的0.2为训练样本,剩余的0.8为测试样本,由此gen_printed_char函数搞完了。
1 | font2image = Font2Image(width, height, need_crop, margin) |
